Contents
Calculation of nonpolar compound concentrations in water (Cw) from passive sampling data can be time consuming and prone to errors. Boost productivity and quality control with user-friendly templates for processing passive sampling data with or without performance reference compounds.
Nonpolar compounds: Cw calculation with PRCs
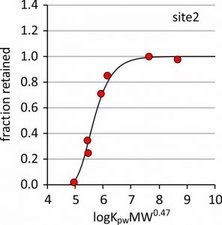
In-situ calibration of uptake kinetics can be done by analyzing dissipation of performance reference compounds (PRCs). Concentrations in water can then be calculated from uptake kinetics and absorbed amounts.
Spreadsheet-based templates optimize passive sampling rates based on PRC dissipation as outlined by Booij and Smedes (2010) and Rusina et al. (2010), and calculate aqueous concentrations.
Available for SPMDs, low-density polyethylene, and silicone samplers.
Features
- Input parameters (copy from your data workbook, paste into template)
- exposure details (exposure ID, sampler mass & area, exposure time)
- retained fractions of performance reference compounds (PRCs)
- accumulated amounts of target analytes
- Output parameters (copy from template, paste into your data workbook)
- Sampling rates with standard errors
- Time-weighted average concentrations
- plots of model results (model fit and residual errors)
- Process 1 to 20 exposures in one run
- Sampler-water partition coefficients included (literature values of commonly used PRCs and nonpolar compounds)
- Target compound list and partition coefficients editable to suit user’s needs.
- Online training included for each purchase.
- Manual with scientific background and operating instructions
- Unlimited copies allowed within customer’s organization
More details: download manual for SSP-M823 silicone (manuals and templates for SPMD and LDPE are similar).
Price: EUR 357, including ~30 min free on-line support to get you started.
Questions/Orders: e-mail info@pasoc.eu ; specify sampler type (silicone/LDPE/SPMD).
Nonpolar compounds: Cw calculation without PRCs
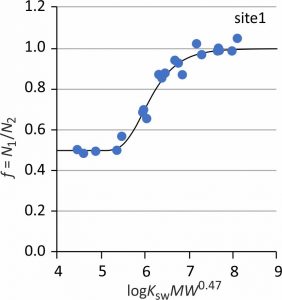
In situ calibration of sampler-water exchange kinetics can also be done by parallel exposure of single-phase polymers with different thickness and same surface area. Compounds with low partition coefficients reach sampler-water equilibrium in both samplers. Ratios of amounts in thin and thick samplers are equal to the ratio of of sampler mass. Compounds with high partition coefficients have amount ratios that are equal to 1 because their uptake is proportional to surface area and is not limited by sampler volume. Sampling rates can be estimated by fitting contaminant mass ratio (CMR) as a function of partition coefficient. Details of the CMR method are given by Fuchte et al. (2020). The CMR-Cw calculation template handles all calculations for you: best-fit sampling rate including standard error, and aqueous concentrations. You only need to fill out (copy/paste) the amounts that are detected in thin and thick samplers.
Features:
- Input parameters (copy from your data workbook, paste into template)
- exposure details (exposure ID, sampler mass & area, exposure time)
- amounts detected in thin and thick samplers
- Output parameters (copy from template, paste into your data workbook)
- Sampling rates with standard errors
- Time-weighted average concentrations
- plots of model results (model fit and residual errors)
- Process 1 to 10 exposures in one run
- Applicable to low-density polyethylene and silicone samplers
- Target compound list and partition coefficients editable to suit user’s needs.
- Online training included for each purchase.
- Manual with scientific background and operating instructions
- Unlimited copies allowed within customer’s organization
More details: download CMR-Cw manual
Price: EUR 357, including ~30 min free support to get you started
Questions/Orders: e-mail info@pasoc.eu